There are several ways to interpret a postgraduate diploma. By name alone, it is clearly a graduate program, just like a graduate-level degree. On the other, it is lacks some requirements to be called an actual degree. Let’s review it in the context of the education system of India.
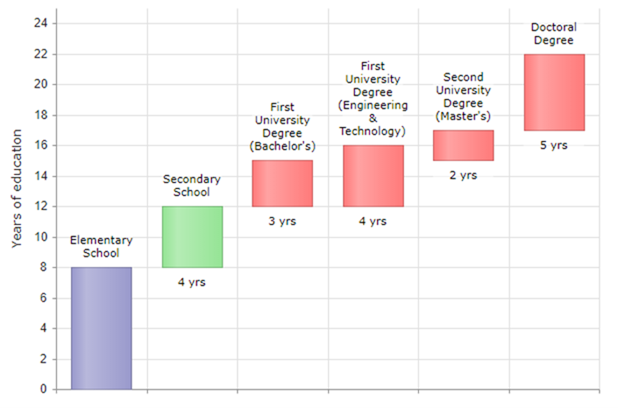 India’s education consists of twelve years of primary and secondary education, three to four years of undergraduate education for a bachelor’s degree, two years of graduate education for a master’s degree, terminating in doctoral degrees. More information can be found on the Inia section of Scholaro Pro.
India’s education consists of twelve years of primary and secondary education, three to four years of undergraduate education for a bachelor’s degree, two years of graduate education for a master’s degree, terminating in doctoral degrees. More information can be found on the Inia section of Scholaro Pro.
Postgraduate diplomas usually require a first university degree (Bachelor’s) for admission, hence their designation as postgraduate. However, evaluating a one-year postgraduate diploma has different results depending on the type of bachelor’s degree that is required for admission. Moreover, when postgraduate diplomas are awarded in fields of study that also have master’s degrees they must somehow differ.
Research conducted by the Association of International Credential Evaluators finds that a bachelor’s degree in the United States requires four years of consecutive post-secondary education. Using the year counting methodology, a three-year Indian bachelor’s degree in arts or science represents the first through third year, and a one-year postgraduate diploma represents the fourth, allowing a US bachelor’s degree equivalency. However, when a postgraduate diploma requires a four-year bachelor’s degree in technology or engineering, it represents the fifth year of consecutive education, and pure year-counting would allow it to be equate to a master’s degree. So, why isn’t it called a master’s degree?
Since a postgraduate diploma is not called “master’s degree”, logic dictates that it must be somehow different than a master’s degree. Most postgraduate diplomas are more applied in nature. Most (with exceptions) do not grant access to further graduate study. They are also most commonly awarded by institutions recognized by the All India Council on Technical Education (AICTE), as opposed to the University Grants Commission (UGC) that oversees universities. One notable exception from the above is management education.
Management education is offered at the graduate level in for form of master’s degrees and postgraduate diplomas. The latter are comprised of two-year postgraduate diplomas, executive postgraduate diplomas, and postgraduate certificates. Although master’s degrees in management are offered by recognized universities, the Association of Indian Universities (AIU) equates the two-year postgraduate diploma in management with a Master of Business Administration degree when it is awarded by one of the approved organizations in the table below. See https://www.aiu.ac.in/evaluation.php for additional information.
In summary, there are some fundamental differences between a master’s degree and a postgraduate diploma. However, in India, conditions exist where some postgraduate diplomas are considered equal to master’s degrees. In these cases, these credentials should be evaluated in the same ways as master’s degrees for an equivalency in the united states or any other foreign country.
Below: Institutions whose Two-Year Full Time Postgraduate Diploma in Management (PGDM)has been equated with MBA Degree for purpose of admission to Higher Education